The beam use in external radiotherapy may be generally grouped into photon or particles. Heavy ion is one kind of particle radiotherapy. The name of “heavy” comes from the fact that the particle it uses is heavier than proton. The most often used particle in heavy ion radiotherapy at the present is carbon ion.
The energy of photon would decrease after entering body in conventional external beam therapy. For deeper tumor, the photon beam would cause damage to the normal tissues it travels by before it reaches the targeted tumor. For particle therapy, the energy it releases may be restricted to right adjacent to the target tumor, and thus sparing the normal tissues. Both as particle therapy, heavy ion has higher Relative Biological Effectiveness (RBE) than proton therapy. RBE of heavy ion is three times than proton, which is around the same as photon. Heavy ion is also better in its nature of not depending on oxygen in tumor control. In another word, it has low oxygen enhancement ratio (OER). For those tumors with severe low concentration of oxygen, or, hypoxia, heavy ion may tackle this situation. By high RBE and low OER, heavy ion therapy may deal with those tumors resisting to conventional external beam radiotherapy.
Currently, the heavy ion facilities and major clinical cases are restricted in only a few sites in Japan and German. Japan has most profound experience in clinical application. For prostate cancer, early lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, bone and soft tissue sarcoma, there have been many positive results published. According to the literature published by National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS) of Japan, the 5-year disease control rate may be up to 80% for hepatocellular carcinoma. [1]。
Taipei Veterans General Hospital and NIRS of Japan have signed Memorandum of Understanding for heavy ion in cancer treatment. We will keep cooperating with and learning from experts of heavy ion from Japan. The plan of building heavy ion center was approval from the Ministry of Health and Welfare on Nov. 30 2015. That center is slated to begin operations in 2019.
[1] Carbon ion radiotherapy in Japan: an assessment of 20 years of clinical experience. Lancet Oncol 2015; 16(2): e93-100.
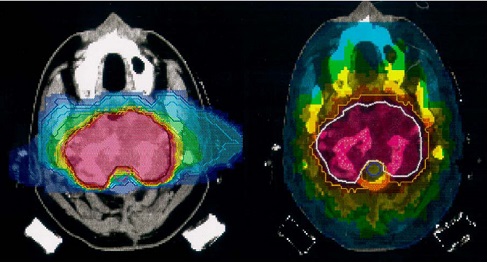
Dose distribution of skull base tumor using heavy ion (Left) and photon(Right). While the dose distribution of heavy ion concentrates to the tumor only, the posterior neck and the oral cavity are almost free from radiation.
Courtesy: Rep. Prog. Phys. 68 (2005) 1861–1882
Last Modified: