 Stroke is a medical emergency caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, which impairs the brain's ability to receive adequate oxygen supply and results in functional impairment. After acute treatment, about 75% of people experience varying degrees of sequelae, with hemiplegia and language barriers being the most common. In severe cases, even assistance from others may be required for daily activities. Therefore, post-stroke rehabilitation is particularly important. The most worrying thing is that after more than six months of rehabilitation, stagnation may occur, and paralysis and disability may become lifelong fates.
Stroke is a medical emergency caused by a blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain, which impairs the brain's ability to receive adequate oxygen supply and results in functional impairment. After acute treatment, about 75% of people experience varying degrees of sequelae, with hemiplegia and language barriers being the most common. In severe cases, even assistance from others may be required for daily activities. Therefore, post-stroke rehabilitation is particularly important. The most worrying thing is that after more than six months of rehabilitation, stagnation may occur, and paralysis and disability may become lifelong fates.
According to Dr. Tsai Po-Yi, Director of Neurorehabilitation at the Rehabilitation Department of Taipei Veterans General Hospital, a new high-tech brain treatment technology called repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has been recently confirmed by the academic community to have excellent therapeutic effects. This is a non-surgical, non-invasive, and painless treatment that has been validated by thousands of clinical experiences, regardless of whether it is in the chronic or acute phase.
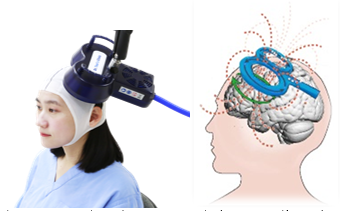
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive neuro-modulation technique that can be used to treat brain-related conditions without surgery.
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) involves the use of a coil, approximately 20 cm in diameter, to produce powerful magnetic pulses that penetrate the skull (without pain). This induces electrical currents in the brain, which can activate damaged areas near the brain or change the connections between the left and right hemispheres, leading to functional improvement. This is a neuro-modulation technique.

Improving difficult-to-treat paralysis of the limbs, speech disorders, cognitive impairments, and swallowing difficulties.
Unlike a broken bone that can be surgically fixed and regrow, brain damage is much more complicated and difficult to regenerate due to the intricate structure of the brain. Therefore, the fear of stroke lies in the difficulty of recovering lost functions. Walking with the lower limbs is critical for future health and longevity, and the inability to express oneself with language can have a huge impact on daily life. Fortunately, scientists have discovered that the brain's plasticity is lifelong. Therefore, by using this feature, magnetic stimulation can shape this commanding brain. The principle behind magnetic stimulation includes increasing the growth of nerve fibers, promoting the secretion of neurotransmitters, improving lymphatic drainage in the brain, and even changing genes.
However, the brain is a very complex and difficult organ to work with, and more stimulation is not necessarily better. Excessive stimulation can actually inhibit the originally promoted signals. If the stimulation intensity is not strong enough, it may be ineffective. Therefore, determining the optimal stimulation parameters and treatment location requires long-term research and tailoring to the individual patient's condition to achieve the best results.
Magnetic stimulation can improve post-stroke sequelae such as paralysis of the limbs, speech disorders, cognitive impairments, and swallowing difficulties. Functions lost after a stroke are difficult to recover, so stroke patients require long-term rehabilitation. Magnetic stimulation utilizes the brain's plasticity to stimulate brain regions, improve nerve fiber growth, promote neurotransmitter secretion, and even change genes, thereby achieving a therapeutic effect. However, the intensity of magnetic stimulation and treatment location need to be tailored to each patient, as excessive or insufficient stimulation can both affect treatment outcomes. Therefore, the optimal magnetic stimulation parameters need to be established through long-term research and individualized treatment plans.
最後更新: